推荐等级:
发布时间: 2021-12-31 10:45
扫码用手机做题
For ()service, we need a virtual-circuit subnet. Let us see how that works. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new()for every packet sent. Instead, when a connection is established, a route from the()machine to the destination machine is chosen as part of the connection setup and stored in tables inside the()That route is used for all traffic flowing over the connection, exactly the same way that the telephone system works. When the connection is released, the virtual circuit is also terminated. With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an()telling which virtual circuit it belongs to.
本题解析:
虚电路相关。
For ()service, we need a virtual-circuit subnet. Let us see how that works. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new()for every packet sent. Instead, when a connection is established, a route from the()machine to the destination machine is chosen as part of the connection setup and stored in tables inside the()That route is used for all traffic flowing over the connection, exactly the same way that the telephone system works. When the connection is released, the virtual circuit is also terminated. With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an()telling which virtual circuit it belongs to.
本题解析:
虚电路相关。
For ()service, we need a virtual-circuit subnet. Let us see how that works. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new()for every packet sent. Instead, when a connection is established, a route from the()machine to the destination machine is chosen as part of the connection setup and stored in tables inside the()That route is used for all traffic flowing over the connection, exactly the same way that the telephone system works. When the connection is released, the virtual circuit is also terminated. With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an()telling which virtual circuit it belongs to.
本题解析:
虚电路相关。
For ()service, we need a virtual-circuit subnet. Let us see how that works. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new()for every packet sent. Instead, when a connection is established, a route from the()machine to the destination machine is chosen as part of the connection setup and stored in tables inside the()That route is used for all traffic flowing over the connection, exactly the same way that the telephone system works. When the connection is released, the virtual circuit is also terminated. With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an()telling which virtual circuit it belongs to.
本题解析:
虚电路相关。
For ()service, we need a virtual-circuit subnet. Let us see how that works. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new()for every packet sent. Instead, when a connection is established, a route from the()machine to the destination machine is chosen as part of the connection setup and stored in tables inside the()That route is used for all traffic flowing over the connection, exactly the same way that the telephone system works. When the connection is released, the virtual circuit is also terminated. With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an()telling which virtual circuit it belongs to.
本题解析:
虚电路相关。
常用的外部网关协议是()。
本题解析:
根据路由选择协议的应用范围,可以将其分为内部网关协议、外部网关协议和核心网关协议三大类。其分类如下图所示:
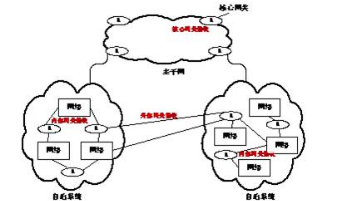
(1)自治系统:是指同构型的网关连接的互联网络,通常是由一个网络管理中心控制的。
(2)内部网关协议(IGP):在一个自治系统内运行的路由选择协议,主要包括RIP、OSPF、IGRP、EIGRP等。
(3)外部网关协议(EGP):是指在两个自治系统之间使用的路由选择协议,最新的EGP协议是BGP,其主要的功能是控制路由策略。
边界网关协议(BGP)是运行于 TCP 上的一种自治系统间路由协议。BGP 是唯一设计来处理因特网的大小的协议,也是唯一能够妥善处理好非路由主机多路连接的协议。BGP 交互系统的主要功能是和其他的 BGP 系统交换网络可达信息。网络可达信息包括可达信息经过的自治系统(AS)清单上的信息。这些信息有效地构造了 AS 互联并由此清除了路由环路,同时在 AS 级别上实施了策略决策。
下列路由器命令中用于激活接口的命令是()。
本题解析:
Router(config-if)#no shutdown # 激活接口 Router(config-if)#end # 退回特权模式 Router(config-if)# switchport mode access #配置端口为静态VLAN访问模式
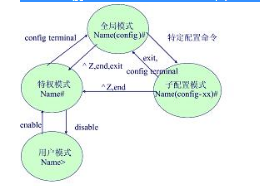
交换机当前状态处于局部配置模式的是()。
本题解析:
交换机配置状态与转换命令。
(1)用户模式:登录到交换机时就会自动进入该模式,这时通常只能够查看,对IOS的运作不会产生任何影响。
(2)特权模式:它可以完成任何事情,包括检查配置文件、重新启动交换机等,它的命令集是用户模式下的超集。
(3)全局配置模式:在该模式下,我们做出的改动会影响IOS的全局运作。
(4)子配置模式:用于对单独的组件进行配置,例如,接口、进程等。
以上四种模式之间的转换命令,如下图所示。
将域名转换成IP地址是由()协议来完成的,将IP地址转换成MAC地址是由()协议来完成的。
本题解析:
IP地址符合了对地址惟一性的需要,Internet上的每一台主机都被分配了一个独立的IP地址,但由于IP地址是用32bit的数字组成,人们记忆起来比较困难,域名就应运而生。域名系统DNS是因特网使用的命名系统,他的功能是用于实现域名与主机地址之间的映射。 ARP协议主要负责将局域网中的32位IP地址转换为对应的48位物理地址,即网卡的MAC地址,比如IP地址为192.168.0.1网卡MAC地址为00-03-0F-FD-1D-2B。整个转换过程是一台主机先向目标主机发送包含IP地址信息的广播数据包,即ARP请求,然后目标主机向该主机发送一个含有IP地址和MAC地址数据包,通过MAC地址两个主机就可以实现数据传输了。
试卷分类:高级系统规划与管理师
练习次数:214次
试卷分类:中级系统集成项目管理工程师
练习次数:225次
试卷分类:中级软件设计师
练习次数:229次
试卷分类:中级网络工程师
练习次数:238次
试卷分类:初级网络管理员
练习次数:226次
试卷分类:中级数据库系统工程师
练习次数:222次
试卷分类:中级软件评测师
练习次数:219次
试卷分类:中级信息安全工程师
练习次数:215次
试卷分类:中级信息安全工程师
练习次数:199次
试卷分类:中级软件设计师
练习次数:208次